|
 |


Mar. 16, 2010 -
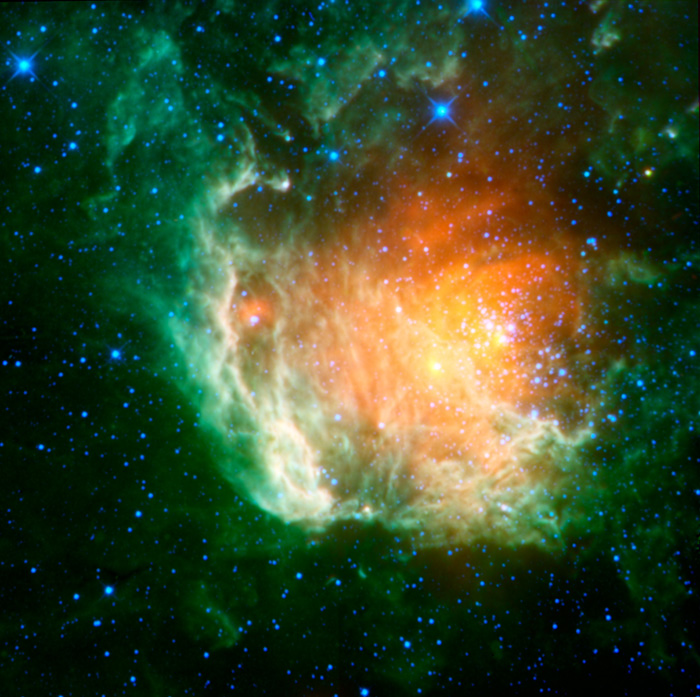
A new infrared image from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, shows a cosmic rosebud blossoming with new stars. The stars, called the Berkeley 59 cluster, are the blue dots to the right of the image center. They are ripening out of the dust cloud from which they formed, and at just a few million years old, are young on stellar time scales.
The rosebud-like red glow surrounding the hot, young stars is warm dust heated by the stars. Green "leafy" nebulosity enfolds the cluster, showing the edges of the dense, dusty cloud. This green material is from heated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, molecules that can be found on Earth in barbecue pits, exhaust pipes and other places where combustion has occurred.
Red sources within the green nebula indicate a second generation of stars forming at the surface of the natal cloud, possibly as a consequence of heating and compression from the younger stars. A supernova remnant associated with this region, called NGC 7822, indicates that a massive star has already exploded, blowing the cloud open in a "champagne flow" and leaving behind this floral remnant. Blue dots sprinkled throughout are foreground stars in our Milky Way galaxy.
Berkeley 59 and NGC 7822 are located in the constellation Cepheus at a distance of about 3,300 light-years from Earth.
Infrared light is color coded in this picture as follows: blue shows 3.4-micron light; cyan, 4.6-micron light; green, 12-micron light; and red, 22-micron light.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/WISE Team |
|