|
 |
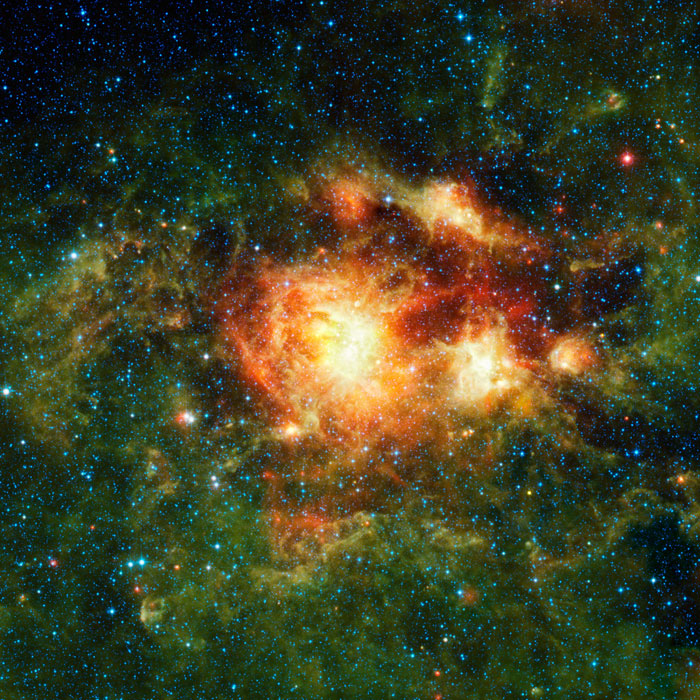


Feb. 17, 2010 - This dramatic image of a nebula containing young, massive stars was captured by NASA's Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, a space telescope mapping the whole sky in infrared light. The nebula, located 20,000 light-years away in the Carina spiral arm of our Milky Way Galaxy, contains a central cluster of huge, hot stars, called NGC3603.
The image was captured using all four of WISE's infrared channels, with longer infrared wavelengths shown in red and green and shorter wavelengths in blue (infrared light of 3.4 and 4.6 microns are blue; 12-micron light is green; and 22-micron light is red).
The cluster contains some of the most massive stars known. Winds and radiation from the stars are evaporating and dispersing the cloud material from which they formed, warming the cold dust and gas surrounding the central nebula. This greenish "halo" of warm cloud material is seen best by WISE due to its large field of view and improved sensitivity over past all-sky infrared surveys.
These WISE observations provide circumstantial evidence that the massive stars in the center of the cluster triggered the formation of younger stars in the halo, which can be seen as red dots. The dust at the center of the cluster is very hot, producing copious amounts of infrared light, which results in the bright, yellow cores of the nebulosity.
Ultimately, this turbulent region will be blasted apart by supernova explosions. Other star-forming clouds in the Milky Way have experienced such eruptions, as evidenced by their pockmarked clouds of expanding cavities and bubbles.
Massive star clusters like this one are an important link to understanding the details of the violent original epoch of massive star formation in the early, distant universe. Astronomers also use them to study distant starbursts that occur when galaxies collide, lighting up tremendous firestorms of brilliant, but ephemeral, stars in the wreckage. Because NGC 3603 is so close, it is an excellent lab for the study of such faraway and momentous events.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/WISE Team
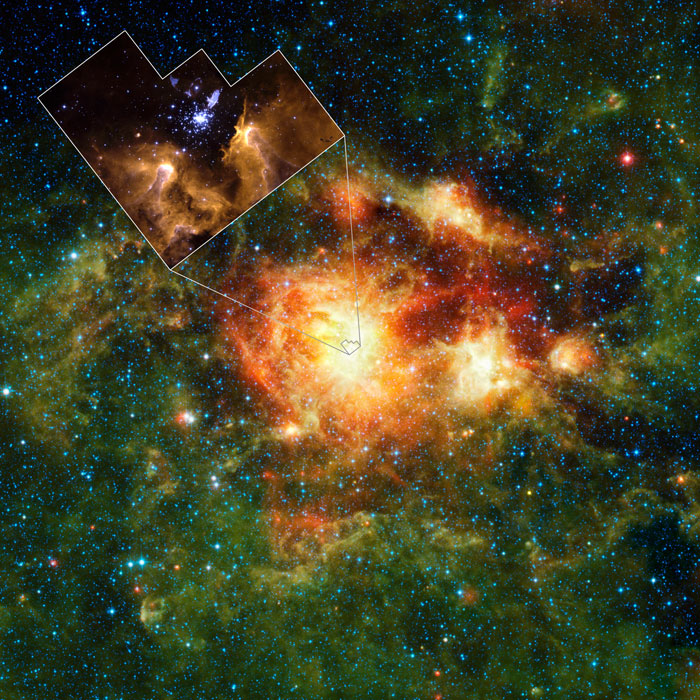

Feb. 17, 2010 - This infrared image taken by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, shows a star-forming cloud teeming with gas, dust and massive newborn stars. The inset reveals the very center fo the cloud, a cluster of stars called NGC 3603. It was taken in visible light by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope.
WISE, which is surveying the whole sky in infrared light, is particularly sensitive to the warm dust that permeates star-forming clouds like this one. In this way, WISE complements visible-light observations.
The mission also complements Hubble and other telescopes by showing the "big picture," providing context for more detailed observation. For example, the WISE picture here is 2,500 times larger than the Hubble inset. While the Hubble view shows the details of the hot young star cluster, the WISE picture shows the effects that this stellar powerhouse has on its neighborhood. The massive stars are heating up and compressing nearby clouds, possibly triggering the birth of new stars.
In the WISE image, infrared light of 3.4 and 4.6 microns are blue; 12-micron light is green; and 22-micron light is red.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA
Hubble credit: NASA/STScI/MPIA/Univ. of Heidelberg/Univ. of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
|
|