

|
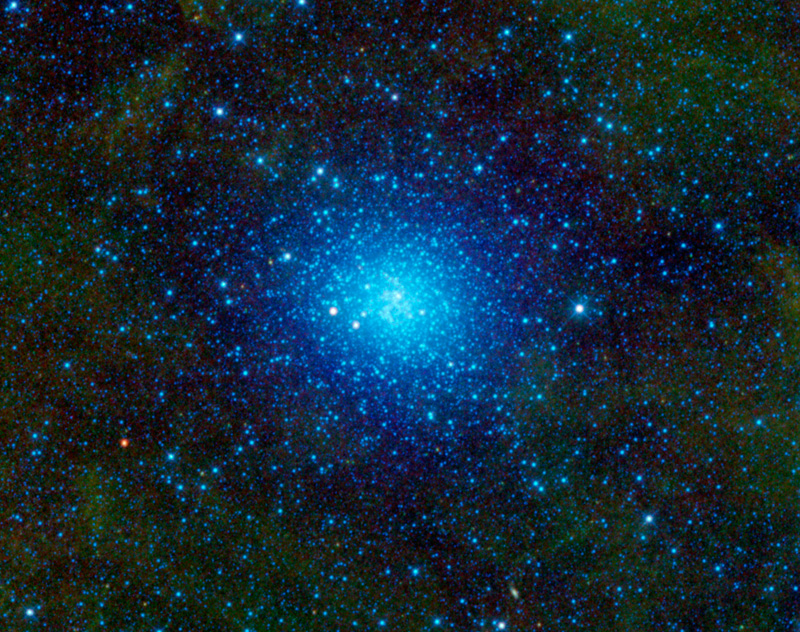
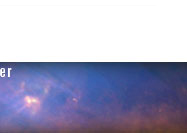
Aug 16, 2010 - Omega Centauri NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, has captured a favorite observing target of amateur astronomers -- Omega Centauri. Also known as NGC 5139, this celestial cluster of stars can be found in the constellation Centaurus and can be seen by the naked eye to observers at low northern latitudes and in the southern hemisphere. Omega Centauri contains approximately 10 million stars and is about 16,000 light-years away. This image spans an area on the sky equivalent to a grid of about 3 by 2 full Moons. The ancient astronomer Ptolemy thought Omega Centauri was a star, and Edmond Halley identified it as a nebula in 1677. In the 1830s, John Herschel identified it as a globular star cluster orbiting the Milky Way Galaxy. A globular cluster is a spherical group of stars that are bound together by gravity. Omega Centauri has always been the black sheep of globular clusters, since it has several characteristics that mark it as different from the typical globular cluster. For example, Omega Centauri is ten times more massive than other globular clusters. It also includes stars of a variety of ages, whereas other globular clusters contain stars from only one generation. Recent research based on observations using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini Observatory indicates that there is a black hole at its center. This suggests that Omega Centauri may actually be a dwarf galaxy that has been stripped of its outer stars and not a globular cluster after all. All four infrared detectors aboard WISE were used to create this mosaic image of Omega Centauri. The colors blue and cyan represent light emitted from stars at wavelengths of 3.4 and 4.6 microns. The green halo surrounding the center represents light at 12 microns, emitted by warm dust. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/WISE Team |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||

