

|
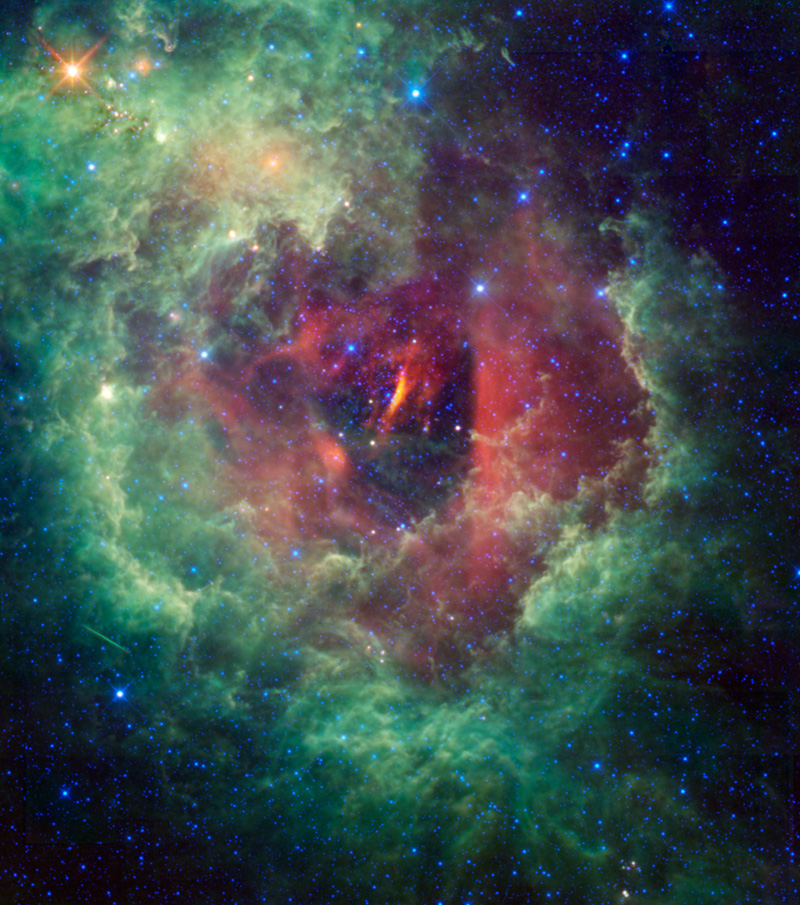
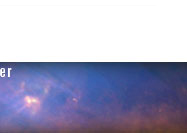
Aug 25, 2010 - WISE Captures the Unicorn's Rose Unicorns and roses are usually the stuff of fairy tales, but a new cosmic image taken by NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Explorer (WISE) shows the Rosette nebula located within the constellation Monoceros, or the Unicorn. This flower-shaped nebula, also known by the less romantic name NGC 2237, is a huge star-forming cloud of dust and gas in the Milky Way Galaxy. Estimates of the nebula’s distance vary from 4,500 to 5,000 light-years away. At the center of the flower is a cluster of young stars called NGC 2244. The most massive stars produce huge amounts of ultraviolet radiation, and blow strong winds that erode away the nearby gas and dust, creating a large, central hole. The radiation also strips electrons from the surrounding hydrogen gas, ionizing it and creating what astronomers call an HII region. Although the Rosette nebula is too faint to see with the naked eye, NGC 2244 is beloved by amateur astronomers because it is visible through a small telescope or good pair of binoculars. The English astronomer John Flamsteed discovered the star cluster NGC 2244 with a telescope around 1690, but the nebula itself was not identified until John Herschel (son of William Herschel, discoverer of infrared light) observed it almost 150 years later. The streak seen at lower left is the trail of a satellite, captured as WISE snapped the multiple frames that make up this view. This image is a four-color composite created by all four of WISE’s infrared detectors. Color is representational: blue and cyan represent infrared light at wavelengths of 3.4 and 4.6 microns, which is dominated by light from stars. Green and red represent light at 12 and 22 microns, which is mostly light from warm dust. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/WISE Team |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||

