


|
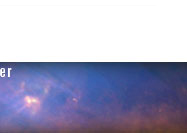
May 20, 2010 - Seagull Nebula - Running with the Big Dog The Seagull nebula, seen in this infrared mosaic from NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, draws its common name from its resemblance to a gull in flight. But it depends on your point of view. When the image is rotated 180 degrees it bears a passing resemblance to a galloping lizard – or perhaps a dragon or a dinosaur. The image spans an area about seven times as wide as the full Moon, and three times as high (3.55 by 1.37 degrees), straddling the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major (the Big Dog). So you might say this lizard is running with the Big Dog, while the gull is flying from it. Astronomers catalog the nebula as IC 2177. This cosmic cloud is one of many sites of star formation within the Milky Way Galaxy. It is located 3,800 light-years away from Earth, inside the Orion spur -- the same partial spiral arm of the Milky Way where our Solar System is located. The nebula is nearly 240 light-years across. Astronomers list the region near the seagull’s eye (or lizard’s hip) as NGC 2327, which contains a cluster of stars born about 1.5 million years ago. The eye is the brightest and hottest of the newborn stars in the entire nebula, and heats up the dust so that it glows in infrared light. All four infrared detectors aboard WISE were used to make this image. Color is representational: blue and cyan represent infrared light at wavelengths of 3.4 and 4.6 microns, which is dominated by light from stars. Green and red represent light at 12 and 22 microns, which is mostly light from warm dust. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/WISE Team |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||


