

|
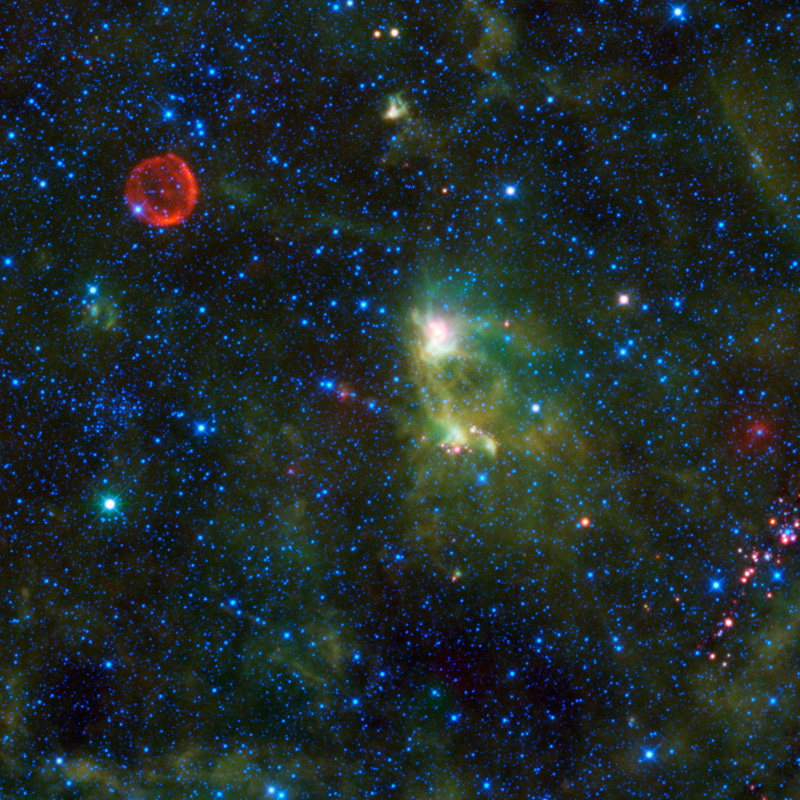
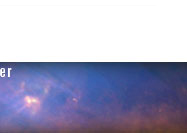
July 9, 2010 - Tycho’s Supernova Remnant This image from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) takes in several interesting objects in the constellation Cassiopeia, none of which are easily seen in visible light. The red circle visible in the upper left part of the image is SN 1572, often called “Tycho’s Supernova”. This remnant of a star explosion is named after the astronomer Tycho Brahe, although he was not the only person to observe and record the supernova. When the supernova first appeared in November 1572, it was as bright as Venus and could be seen in the daytime. Over the next two years, the supernova dimmed until it could no longer be seen with the naked eye. It wasn’t until the 1950s that the remnants of the supernova could be seen again with the help of telescopes. When the star exploded, it sent out a blast wave into the surrounding material, scooping up interstellar dust and gas as it went, like a snow plow. An expanding shock wave traveled into the surroundings and a reverse shock was driven back into toward the remnants of the star. Previous observations by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope indicate that the nature of the light that WISE sees from the supernova remnant is emission from dust heated by the shock wave. In the center of the image is a star forming nebula of dust and gas, called S175 (in the Sharpless catalog of ionized nebula). This cloud of material is about 3,500 light years away and 35 light-years across. It is being heated by radiation from young hot stars within it, and the dust within the cloud radiates infrared light. On the left edge of the image, between the Tycho supernova remnant and the very bright star, is an open cluster of stars, King 1, first catalogued by Ivan King, an astronomer at UC Berkeley. This cluster is about 6,000 light-years away, 4 light-years across and is about 2 billion years old. Also of interest in the lower right of the image is a cluster of very red sources. Almost all of these sources have no counterparts in visible light images, and only some have been catalogued by previous infrared surveys. There are indications that they may be young stellar objects associated with a dense nebula in the area. Young stellar objects (YSOs) are stars in their earliest stages of life. YSOs are surrounded by an envelope of dust, which would explain the very red color of the sources in this image. All four infrared detectors aboard WISE were used to make this mosaic. The image spans an area of 1.6 x 1.6 degrees on the sky or about 3 times as wide and high as the full Moon. Color is representational: blue and cyan represent infrared light at wavelengths of 3.4 and 4.6 microns, which is dominated by light from stars. Green and red represent light at 12 and 22 microns, which is mostly light from warm dust. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/WISE Team |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||

