
|
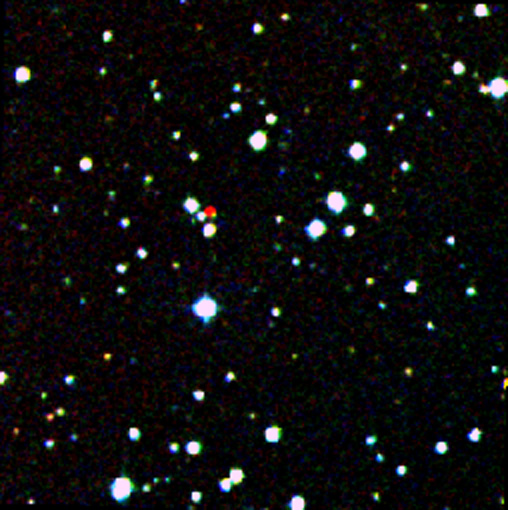
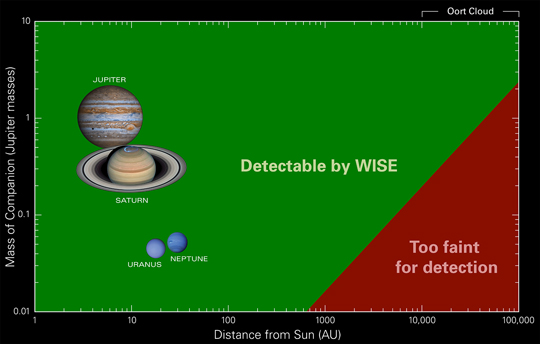
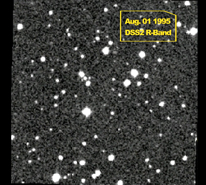
NASA's WISE Survey Finds Thousands of New Stars, But No 'Planet X [Scroll down for images and video.] After searching hundreds of millions of objects across our sky, NASA's Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) has turned up no evidence of the hypothesized celestial body in our solar system commonly dubbed "Planet X." Researchers previously had theorized about the existence of this large, but unseen celestial body, suspected to lie somewhere beyond the orbit of Pluto. In addition to "Planet X," the body had garnered other nicknames, including "Nemesis" and "Tyche." This recent study, which involved an examination of WISE data covering the entire sky in infrared light, found no object the size of Saturn or larger exists out to a distance of 10,000 astronomical units (au), and no object larger than Jupiter exists out to 26,000 au. One astronomical unit equals 93 million miles. Earth is 1 au, and Pluto about 40 au, from the sun. "The outer solar system probably does not contain a large gas giant planet, or a small, companion star," said Kevin Luhman of the Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds at Penn State University, University Park, Pa., author of a paper in the Astrophysical Journal describing the results. But searches of the WISE catalog are not coming up empty. A second study reveals several thousand new residents in our sun's "backyard," consisting of stars and cool bodies called brown dwarfs. "Neighboring star systems that have been hiding in plain sight just jump out in the WISE data," said Ned Wright of the University of California, Los Angeles, the principal investigator of the mission. The second WISE study, which concentrated on objects beyond our solar system, found 3,525 stars and brown dwarfs within 500 light-years of our sun. "We're finding objects that were totally overlooked before," said Davy Kirkpatrick of NASA's Infrared and Processing Analysis Center at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif. Kirkpatrick is lead author of the second paper, also in the Astrophysical Journal. Some of these 3,525 objects also were found in the Luhman study, which catalogued 762 objects. The WISE mission operated from 2010 through early 2011, during which time it performed two full scans of the sky -- with essentially a six-month gap between scans. The survey captured images of nearly 750 million asteroids, stars and galaxies. In November 2013, NASA released data from the AllWISE program, which now enables astronomers to compare the two full-sky surveys to look for moving objects. In general, the more an object in the WISE images appears to move over time, the closer it is. This visual clue is the same effect at work when one observes a plane flying low to the ground versus the same plane flying at higher altitude. Though traveling at the same speed, the plane at higher altitude will appear to be moving more slowly. Searches of the WISE data catalog for these moving objects are uncovering some of the closest stars. The discoveries include a star located about 20 light-years away in the constellation Norma, and as reported last March, a pair of brown dwarfs only 6.5 light-years away -- making it the closest star system to be discovered in nearly a century. Despite the large number of new solar neighbors found by WISE, "Planet X" did not show up. Previous speculations about this hypothesized body stemmed in part from geological studies that suggested a regular timing associated with mass extinctions on Earth. The idea was that a large planet or small star hidden in the farthest reaches of our solar system might periodically sweep through bands of outer comets, sending them flying toward our planet. The Planet X-based mass extinction theories were largely ruled out even prior to the new WISE study. Other theories based on irregular comet orbits had also postulated a Planet X-type body. The new WISE study now argues against these theories as well. Both of the WISE searches were able to find objects the other missed, suggesting many other celestial bodies likely await discovery in the WISE data. "We think there are even more stars out there left to find with WISE. We don't know our own sun's backyard as well as you might think," said Wright. WISE was put into hibernation upon completing its primary mission in 2011. In September 2013, it was reactivated, renamed NEOWISE and assigned a new mission to assist NASA's efforts to identify the population of potentially hazardous near-Earth objects. NEOWISE will also characterize previously known asteroids and comets to better understand their sizes and compositions. JPL managed and operated WISE for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. The mission was selected competitively under NASA's Explorers Program managed by the agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The science instrument was built by the Space Dynamics Laboratory in Logan, Utah. The spacecraft was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colo. Science operations and data processing take place at the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. More information is online at: http://www.nasa.gov/wise and http://wise.astro.ucla.edu and http://jpl.nasa.gov/wise.Image Credit: Penn State University What WISE Can and Cannot See Data from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, has found no evidence for a hypothesized body sometimes referred to as "Planet X." This body was thought to be a large planet or small star orbiting in the far reaches of our solar system. Astronomers searched millions of images taken by WISE over the whole sky, finding no Saturn-like body out to a distance of 10,000 astronomical units (au) from the sun, and no Jupiter-like body out to 26,000 au. One astronomical unit equals 93 million miles. Earth is 1 au, and Pluto about 40 au, from the sun. This chart shows what types of objects WISE can and cannot see at certain distances from our sun. Bodies with larger masses are brighter, and therefore can be seen at greater distances. For example, if a Jupiter-mass planet existed at 10,000 au, WISE would have easily seen it. But WISE would not have been able to see a Jupiter-mass planet residing at 100,000 au -- it would have been too faint. The chart was created by Janella Williams of Penn State University, University Park, PA. WISE was put into hibernation upon completing its primary mission in 2011. In September 2013, it was reactivated, renamed NEOWISE and assigned a new mission to assist NASA's efforts to identify the population of potentially hazardous near-Earth objects. NEOWISE will also characterize previously known asteroids and comets to better understand their sizes and compositions. A New Solar Neighbor Image credit: DSS/NASA/JPL-Caltech A nearby star stands out in red in this image from the Second Generation Digitized Sky Survey. The star, called WISEA J204027.30+695924.1, was initially discovered using data from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), which scanned the entire sky in infrared light in 2010 and early 2011, before ending its primary mission. Objects that are close to us will appear to move more than distant objects when viewed over time. By comparing images taken by WISE six months apart, astronomers are finding thousands of stars and brown dwarfs in our sun's "backyard."
Video Caption: The motion of one of the new neighboring stars discovered by NASA's
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) over more than 50 years can
be seen in this animation, which shows where the star was in photos
taken as early as 1953.
The projected path of the fast-moving, nearby star, dubbed WISEA
J204027.30+695924.1 is shown. This object belongs to a rare class of
old stars known as "L subdwarfs," which are moving with high speed due
to their many gravitational encounters with larger objects over the
course of their lifetimes. The artists' animation shows the L subdwarf
as it would appear to the human eye. Pauses within the animation show
actual, archival data on which the object was recovered after its
discovery in 2014 by WISE. These archival images correspond to the
First Generation Digitized Sky Survey (DSS1) from 1953, the Second
Generation Digitized Sky Survey
(DSS2) from 1995 and 1996, the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) from
1999, and WISE itself, from 2010. The field of view is 5 arcminutes on
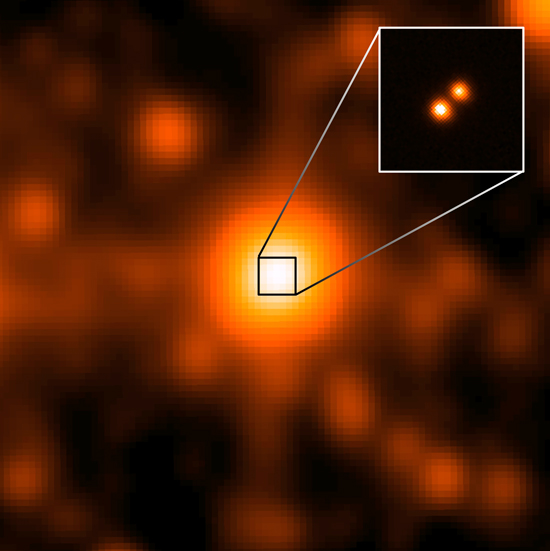
a side with north up and east to the left. This image is color coded as blue (B-band, 4,500 Angstroms), green (R-band, 6,600 Angstroms), and red (I-band, 8,000 Angstroms). The field is five by five arcminutes on a side with north up and east to the left. The Second Generation Digitized Sky Survey images were made from digitized versions of photographic plates taken by the Palomar Observatory near San Diego, CA. Brown Dwarfs in our 'Backyard' Image Credit: NASA/JPL/Gemini Observatory/AURA/NSF The third closest star system to the sun, called WISE J104915.57-531906, is at the center of the larger image, which was taken by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE). It appeared to be a single object, but a sharper image from Gemini Observatory in Chile (inset), revealed that it was binary star system, consisting of a pair of brown dwarfs. This is the closest star system to be discovered in nearly a century. The discovery was announced in March, 2013.
|
|
|||